In today’s modern world, where every home relies heavily on electricity, power outages can be more than just an inconvenience—they can disrupt work, cause food spoilage, and even compromise safety systems. Home battery backup systems have become the go-to solution for ensuring continuous power supply during blackouts. These systems store electrical energy in high-capacity lithium-ion batteries and release it when the grid goes down. They also offer energy independence, reduce electricity costs, and integrate seamlessly with solar panels. Brands like BLUETTI are leading this space with powerful and modular backup systems designed for both home and portable use.
Home battery backup systems like the BLUETTI AC300 and B300 provide reliable, silent power during outages while supporting solar charging and energy independence. Their modular design, high surge capacity, and UPS functionality make them ideal for modern homes with high electrical demands. When paired with proper wire sizing and code-compliant installation, these systems deliver safe, efficient, and future-ready backup power
In this article, we discuss the topic of “wire size for 40 amp breaker“.
BLUETTI AC300 Overview
The BLUETTI AC300 is an advanced modular power station designed for whole-home energy backup. Unlike traditional fixed systems, it allows users to expand their energy storage capacity by connecting additional battery modules. The AC300 is a pure sine wave inverter rated at 3000W, capable of powering multiple household appliances simultaneously. It features a smart touch display, multiple output ports, and a range of charging options. Its modular design ensures easy maintenance and future upgrades, making it ideal for homeowners who want flexibility and scalability.
BLUETTI B300 Home Battery Backup
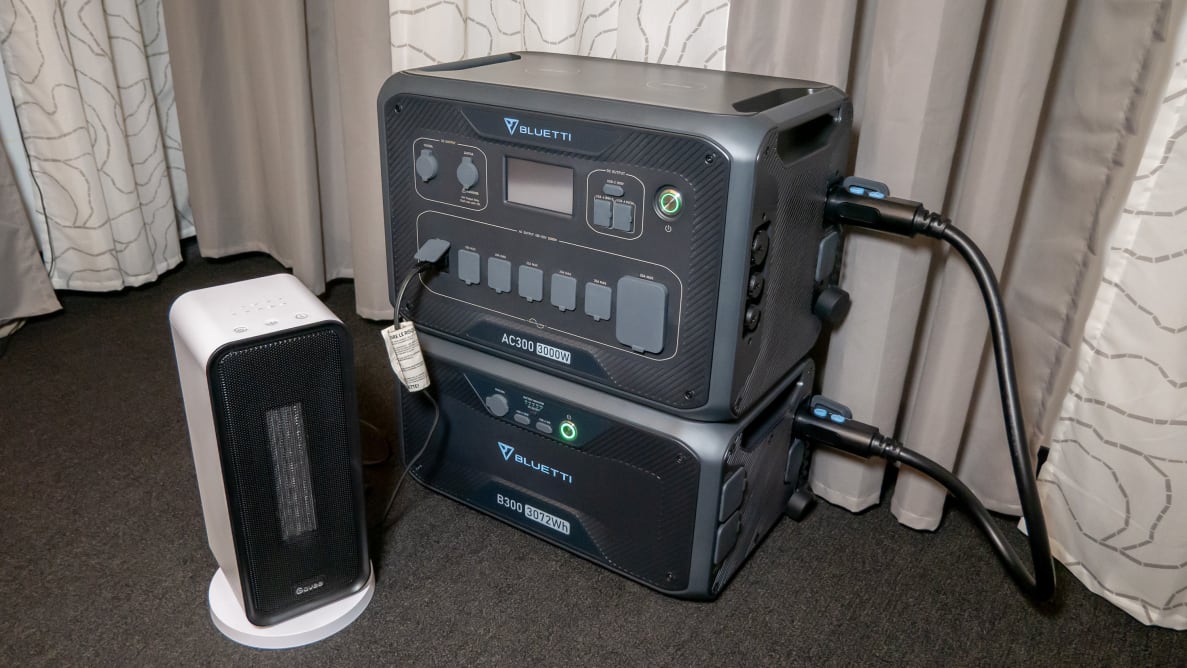

The BLUETTI B300 is the companion battery module to the AC300, built with ultra-durable lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) cells known for safety and longevity. Each B300 module offers a massive 3072Wh of capacity, ensuring long runtime for essential devices during extended outages. The B300 includes its own management system for enhanced battery health and supports DC output, USB ports, and even solar input. When paired with the AC300, the B300 becomes a reliable energy reservoir capable of sustaining critical home loads for hours or even days.
Capacity of BLUETTI AC300 + B300
When combined, the AC300 + B300 setup offers immense energy storage potential. A single AC300 unit can connect up to four B300 battery modules, giving a total capacity of over 12,288Wh (12.3 kWh). This allows homeowners to power essential circuits such as refrigerators, lighting, Wi-Fi routers, and heating or cooling systems. For larger homes or off-grid setups, multiple AC300 systems can even be linked together for expanded capacity. This modularity gives users control over how much storage they want to invest in, ensuring adaptability for different energy needs.
Expandable Battery Options
One of the standout advantages of the BLUETTI ecosystem is expandability. With modular batteries like the B300 and optional B300S units, users can scale their power systems effortlessly. Whether you need backup for a small cabin or an entire home, you can add or remove battery modules as required. This scalability reduces initial costs while allowing future expansion as energy needs grow. The smart battery management system (BMS) ensures that all connected batteries charge and discharge evenly, protecting the lifespan of each module.
Surge Power Capabilities
Every household appliance has a startup surge—the brief moment when devices draw extra current to power on. The BLUETTI AC300 is engineered to handle these surges with ease. With a continuous power rating of 3000W and a surge capacity of up to 6000W, it can comfortably power devices like air conditioners, refrigerators, microwaves, and sump pumps without tripping. This capability makes the AC300 a true home-grade backup power source, not just a portable generator.
24/7 UPS Functionality
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) functionality is a critical feature for any home battery backup system. The AC300 offers 24/7 UPS protection, automatically switching to battery power in under 20 milliseconds when the grid fails. This ensures computers, medical devices, and sensitive electronics remain powered without interruption. Unlike fuel generators that take time to start, the AC300 provides instant, silent power transfer, keeping your home running smoothly no matter what happens to the grid.
Ways to Recharge Your Battery
BLUETTI offers multiple methods to recharge the AC300 and B300 system, ensuring flexibility and convenience. Whether you’re at home, off-grid, or on the road, the system can recharge through AC power, solar panels, car adapters, or even gas generators. Advanced users can also combine power sources for faster recharging. This versatility makes the AC300 ideal for different scenarios—from grid-tied households to remote cabins or RVs.
Charging via AC Power
The most straightforward way to recharge your BLUETTI system is via a standard AC wall outlet. The AC300 supports up to 3000W of AC input, allowing a full charge in just a few hours. Simply plug it into a household circuit, and the intelligent charging system manages current flow to prevent overload. For homeowners with time-of-use electricity rates, charging during off-peak hours can significantly reduce energy costs.
Solar Charging for Home Batteries
Solar charging is one of the key strengths of the BLUETTI AC300. With a maximum solar input of 2400W, the system efficiently converts sunlight into usable power using MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) technology. This allows homeowners to build a completely renewable and self-sufficient power setup. By combining rooftop panels with the AC300, energy independence becomes a reality—reducing reliance on the grid and minimizing electricity bills.
Recharging via Car Adapter
When traveling or camping, the AC300 can recharge directly from a car’s 12V or 24V DC socket using the appropriate cable. While slower than AC or solar charging, it’s a convenient backup option in emergencies. This feature ensures that your system stays functional even when traditional charging methods are unavailable.
Generator Charging
For extended outages, a gas or diesel generator can recharge the BLUETTI system. The AC300 is compatible with most conventional generators and can regulate input current to prevent damage. Pairing a generator with the battery backup system provides continuous power for long-term blackouts—once the batteries are charged, the generator can be turned off to save fuel and reduce noise.
Using Lead-Acid Batteries
The AC300 can also interface with lead-acid batteries, though this setup requires proper voltage matching and connection through compatible ports. While lithium-ion options like the B300 are more efficient, lead-acid compatibility provides flexibility for users who already have such batteries in their systems
Dual AC Input Charging
For those who need faster turnaround times, the AC300 supports dual AC input charging, effectively doubling the charging speed. With two independent AC sources, the system can achieve a combined input rate that recharges even the largest setups in record time.
AC + Solar Combined Charging
Combining AC and solar charging offers the fastest and most efficient way to recharge the BLUETTI system. The AC300 can simultaneously accept input from both sources, reaching up to 5400W of total charging power. This hybrid mode ensures maximum uptime for critical home systems and is perfect for areas with inconsistent sunlight.
BLUETTI AC300 Pricing and Purchase Options
Pricing for the BLUETTI AC300 varies depending on the number of connected B300 batteries and any promotional bundles. Typically, the AC300 + one B300 module starts around $3,000–$3,500, while multi-battery configurations can exceed $8,000. BLUETTI often offers discounts during seasonal sales or crowdfunding campaigns. Buyers can purchase directly from BLUETTI’s official website, authorized retailers, or select e-commerce platforms. Despite the investment, the long-term energy savings and blackout protection make it a valuable addition to any modern home.
Overview of 40 Amp Circuits
To effectively connect powerful devices like home battery systems or electric appliances, understanding 40 Amp circuits is essential. These circuits are designed to handle higher electrical loads safely without overheating wires or tripping breakers. They are commonly used for heavy-duty equipment that requires more power than standard 15 or 20 Amp outlets can supply.
What is a 40 Amp Breaker?
A 40 Amp breaker is a protective device installed in an electrical panel that allows up to 40 amps of current to flow before tripping. It safeguards both the wiring and connected equipment from overload or short-circuit damage. These breakers are essential for appliances like electric ovens, water heaters, or large AC units. Using the correct breaker rating ensures safety and compliance with electrical codes.
Importance of Correct Wire Size
Choosing the correct wire size for a 40 Amp circuit is crucial to prevent overheating and fire hazards. If the wire gauge is too small, resistance increases, causing the wire to heat up and potentially melt. Conversely, oversizing wires adds unnecessary cost and makes installation difficult. Proper wire sizing ensures safe current flow and efficient energy delivery to your devices.
Determining Wire Size for 40 Amps
Determining the correct wire size for a 40 Amp circuit depends on several factors such as voltage, wire type, and the total length of the run. Generally, for short runs under 100 feet, a 8 AWG copper wire is suitable for a 40 Amp load. However, if the distance increases or if aluminum wire is used, adjustments must be made to compensate for voltage drop. The longer the wire, the thicker it needs to be to ensure efficient current flow and minimize energy loss. Always consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) or a licensed electrician for final sizing recommendations.
120 Volt Single-Phase Circuits
In a 120V single-phase circuit, power is supplied using one hot wire and one neutral wire. These are commonly used for residential lighting and small appliances but can support larger loads when wired correctly. A 40 Amp, 120V circuit is relatively rare because such high current is usually better managed at 240V. However, when required, the proper wire gauge and breaker type must be used to ensure safe operation. Load balancing and correct grounding are especially important at this voltage level.
Wire Size Recommendation for 120V Circuits
For a 120V 40 Amp circuit, a 8 AWG copper wire or 6 AWG aluminum wire is typically recommended. This ensures that the conductor can safely carry the current without overheating. If the total wire length exceeds 100 feet, the wire size should be increased to 6 AWG copper to prevent excessive voltage drop. Using high-quality insulation rated for 90°C or higher is also advised for improved safety and efficiency.
240 Volt Single-Phase Circuits
A 240V single-phase circuit delivers more power with lower current draw, making it ideal for heavy-duty appliances like stoves, water heaters, and large power tools. It uses two hot wires and a ground connection, eliminating the need for a neutral wire in many cases. Because the voltage is doubled, current flow is halved for the same wattage, reducing resistance losses and allowing smaller wires for the same power rating. This setup is common in residential power systems for major appliances and backup battery integration.
Wire Size Recommendation for 240V Circuits
For a 240V 40 Amp circuit, the standard recommendation remains 8 AWG copper or 6 AWG aluminum conductors. The higher voltage helps minimize current loss, allowing efficient power transfer to heavy equipment. As with all circuits, the wire insulation type and installation environment must comply with local and national electrical standards. When in doubt, it’s best to use a slightly thicker wire gauge to ensure safety and future-proofing against additional loads.
Three-Phase Circuits
Three-phase circuits are commonly found in industrial and commercial settings rather than in residential homes. They provide smoother power delivery and greater efficiency for large electrical systems. A 40 Amp three-phase circuit can handle significantly more power than a single-phase circuit because of how the electrical loads are distributed across the three phases. This configuration reduces wear on motors and other equipment, making it ideal for high-performance systems or workshop setups.
Wire Size Recommendation for Three-Phase Circuits
For a 40 Amp three-phase system, 8 AWG copper wire is again the standard, though in long-distance or high-temperature conditions, upgrading to 6 AWG may be necessary. Since three-phase power divides the load across three conductors, total efficiency improves, and voltage drop effects are reduced. Still, accurate wire sizing using NEC ampacity tables ensures compliance and reliability under continuous operation.
Steps to Calculate Wire Size
Calculating wire size involves determining voltage, amperage, distance, and wire material. First, identify the circuit voltage (120V, 240V, or three-phase). Next, confirm the maximum current load—in this case, 40 Amps. Then, use an ampacity chart to match the appropriate wire gauge. For long runs, adjust the wire size upward to offset voltage drop. Finally, ensure the chosen wire type—copper or aluminum—meets NEC and manufacturer standards for the intended application.
Determining Circuit Voltage
Circuit voltage determines how efficiently electricity can travel through wires. In North America, most homes operate with 120V and 240V options, depending on the appliance type. Higher voltage circuits carry more power using less current, allowing for smaller wires and greater efficiency. When connecting a 40 Amp breaker, knowing whether the circuit operates at 120V, 240V, or three-phase is the first step toward proper wire sizing and system design.
Calculating Amperage
Amperage measures the amount of electrical current flowing through a circuit. To calculate it, divide the total wattage by the voltage: Amps = Watts ÷ Volts. For example, a 9600W appliance on a 240V circuit draws 40 Amps. Ensuring that the wire and breaker can handle this amperage continuously without overheating is vital. It’s also good practice to apply the 80% rule, meaning continuous loads should not exceed 32A on a 40A breaker to maintain safety margins.
Using an Ampacity Chart
An ampacity chart lists how much current each wire gauge can safely carry based on insulation type, temperature rating, and installation conditions. Electricians use these charts to select the correct conductor size for a given load. For 40 Amps, 8 AWG copper wire typically fits within the recommended range for most residential applications. Ampacity charts are updated regularly to reflect NEC standards, ensuring consistent safety practices across installations.
Considering Wire Length
Longer wire runs introduce voltage drop, which reduces electrical efficiency and can cause appliances to underperform. As a rule of thumb, if the distance from the breaker panel to the appliance exceeds 100 feet, increase the wire size by one or two gauges. For example, instead of 8 AWG, you might use 6 AWG copper. Maintaining voltage stability ensures your devices operate correctly, and it prevents strain on your backup battery or inverter system.
Choosing Wire Type
Different environments call for different wire types. Common residential wires include THHN, NM-B (Romex), and UF-B for underground use. Outdoor or high-heat areas require wire rated for tougher insulation. When connecting to a home battery backup system like BLUETTI’s, stranded copper wire is preferred because it’s flexible and easy to route through terminals. Always verify that the insulation matches the operating temperature and installation method to maintain code compliance.
Copper vs Aluminum Wire for 40 Amp Circuits
Both copper and aluminum conductors can safely carry 40 Amps, but they differ in conductivity, durability, and cost. Copper wire offers higher conductivity and less voltage drop, making it ideal for shorter, high-performance runs. Aluminum wire, though lighter and cheaper, requires larger diameters to carry the same current and must be terminated with anti-oxidizing compounds to prevent corrosion. Choosing between the two depends on budget, length of the circuit, and environmental factors.
Advantages of Copper Wire
Copper’s superior electrical conductivity allows for smaller wire sizes and reduced energy loss. It is also more durable, resistant to oxidation, and easier to terminate securely in lugs or panels. Copper’s flexibility makes installation simpler, especially in confined spaces. Though it costs more upfront, it typically lasts longer and performs more reliably in demanding conditions. For most residential 40 Amp circuits, copper remains the gold standard.
Disadvantages of Copper Wire
The main drawback of copper wire is its high cost compared to aluminum. It is also heavier, making long runs more challenging to install. In large-scale projects, this added weight and expense can become significant. Additionally, copper theft has been an issue in some areas, requiring secure installation. Despite these downsides, most electricians still favor copper for its reliability and safety
Advantages of Aluminum Wire
Aluminum wire is lighter, more affordable, and easier to install in long-distance applications. It’s ideal for budget-conscious homeowners and large feeders from service panels to subpanels. When properly installed with anti-oxidant compound and aluminum-rated connectors, it can perform safely for decades. Its cost-effectiveness makes it popular for long feeder runs where copper might be too expensive.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Wire

Aluminum wire has higher electrical resistance and can expand or contract with temperature changes, potentially loosening connections. It’s also more prone to oxidation, which increases resistance and heat buildup if left untreated. Improper terminations can lead to overheating or arcing. For these reasons, aluminum must always be used with the correct connectors and inspected periodically for tightness and corrosion.
Comparing Copper and Aluminum Wire
When comparing both metals, copper wins on performance, while aluminum wins on cost and weight. A properly installed aluminum system can be safe and effective, but copper remains preferred for circuits with continuous loads or sensitive equipment. Ultimately, the choice depends on your application, distance, and budget. Consulting an electrician ensures that the selected wire type meets both NEC code and safety standards for your specific installation.
AWG vs SWG Wire Gauge Systems
Wire sizes are measured using two main systems: American Wire Gauge (AWG) and Standard Wire Gauge (SWG). AWG is common in North America, while SWG is used primarily in the UK and some Commonwealth countries. Understanding the difference is vital when interpreting wire charts or importing electrical equipment. Each system uses different numeric values for the same wire diameters, so accurate conversion is important when designing circuits.
Conclusion
Home battery backup systems like the BLUETTI AC300 and B300 represent the future of residential energy storage. They provide a dependable, silent, and eco-friendly solution to blackouts and rising electricity costs. With features such as modular expandability, 24/7 UPS functionality, and multiple recharging options—including solar power—these systems give homeowners greater control over their energy usage and independence from the grid.
Understanding the basics of electrical circuits, including 40 Amp breakers, wire sizing, and safety codes, is equally crucial when integrating these systems into your home. Choosing the correct wire gauge, ensuring proper installation, and following NEC and local regulations all contribute to safety and efficiency.
Ultimately, combining advanced energy storage like BLUETTI’s with sound electrical design allows you to create a reliable, sustainable home power network. Whether you’re preparing for emergencies, living off-grid, or simply wanting to reduce your carbon footprint, these technologies empower you to keep the lights on—no matter what happens outside.
FAQs
1. What is the main advantage of a home battery backup system?
A home battery backup system stores electricity for use during power outages or peak demand times. It keeps essential devices running without relying on noisy fuel generators. Systems like the BLUETTI AC300 also help lower energy bills by storing cheaper, off-peak power or excess solar energy for later use.
2. How long can a BLUETTI AC300 + B300 setup power a home?
Runtime depends on total capacity and the devices connected. A single AC300 with one B300 battery (3072Wh) can power essentials like lighting, a refrigerator, and Wi-Fi for several hours. Expanding to four B300 batteries (over 12kWh) can sustain a typical home for 1–2 days, or much longer if paired with solar panels.
3. Is solar charging faster than AC charging?
Not necessarily. Solar charging speed depends on sunlight intensity and panel wattage. The AC300 can accept up to 2400W of solar input, while AC wall charging supports 3000W or more with dual inputs. Combining AC and solar charging offers the fastest overall recharging time.
4. Can I use the AC300 system off-grid?
Yes. The AC300 and B300 are designed for both on-grid and off-grid operation. With solar panels and adequate storage capacity, you can build a completely self-sufficient energy system that powers your cabin, RV, or remote home without any grid connection.
5. What wire size should I use for a 40 Amp circuit?
For most installations, 8 AWG copper or 6 AWG aluminum wire is recommended for a 40 Amp breaker. If the distance from the breaker panel exceeds 100 feet, increase to a thicker wire to reduce voltage drop. Always confirm with a licensed electrician before final installation.
6. Why is the correct wire size so important?
Incorrect wire sizing can lead to overheating, energy loss, and even electrical fires. The right gauge ensures that current flows safely and efficiently. Following NEC guidelines and local building codes is essential for both safety and insurance compliance.
7. What appliances commonly use 40 Amp breakers?
Appliances that draw significant power—such as electric ranges, ovens, dryers, large AC units, and welders—often require 40 Amp circuits. Some home backup systems and EV chargers may also operate on 40A circuits, depending on their configuration.
8. Can I install a BLUETTI home backup system myself?
While BLUETTI systems are designed for user-friendly setup, connecting them directly to a home circuit or breaker panel should always be done by a licensed electrician. Professional installation ensures compliance with safety standards and prevents potential warranty issues.
9. How long does a BLUETTI battery last?
BLUETTI uses LiFePO₄ (lithium iron phosphate) batteries rated for over 3,500–5,000 charge cycles before reaching 80% capacity. In typical home use, this translates to 8–10 years or more of reliable operation. Proper charging habits and moderate temperatures extend battery life further.
10. Are BLUETTI systems compatible with other solar panels?
Yes. The AC300 supports a wide range of solar panels as long as they meet the correct voltage and current specifications. Using high-efficiency monocrystalline panels with an appropriate MC4 connector ensures optimal performance and charging speed.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on premiumtechy!



