Choosing the correct wire size for your electric dryer is essential for both safety and efficiency. Dryer wire size ensures that your appliance receives the proper amount of electricity without overheating the wires or tripping breakers. Using the wrong wire can lead to frequent circuit interruptions, increased energy consumption, or even electrical hazards. This guide covers everything from amperage requirements to types of cables suitable for dryers. Whether you are installing a new dryer or replacing an old circuit, understanding wire size is the first step toward a safe and reliable installation.
Choosing the correct dryer wire size is essential for safe and efficient operation. Most electric dryers require a dedicated 240V circuit, typically using 10 AWG copper wire for 30-amp dryers, with larger gauges for higher amperage models. Following NEC guidelines, using the right breaker, and upgrading to a 4-prong outlet ensures maximum safety, performance, and code compliance.
In this article, we discuss the topic of “dryer wire size“.
Why Choosing the Right Wire Size Matters for Your Dryer

The right wire size ensures that your dryer operates safely and efficiently. Undersized wires can overheat, causing insulation to melt and potentially leading to electrical fires. Oversized wires, while safer, are harder to handle and may increase installation costs unnecessarily. Selecting the proper wire size also prevents breaker trips, maintains optimal dryer performance, and ensures compliance with the National Electric Code (NEC). Homeowners often underestimate the importance of wire gauge, but it directly impacts both safety and longevity of your electrical system.
Understanding Electric Dryer Circuits
Electric dryers typically require a dedicated circuit, separate from other household appliances. These circuits provide consistent power to operate high-demand components such as heating elements and motors. Dryers usually run on 220V or 240V circuits, though older models may use 110V or 120V. Understanding the requirements of a dryer circuit, including amperage, voltage, and grounding, is vital for proper installation. Proper circuit design ensures energy efficiency, reduces fire risks, and meets local electrical codes.
How Many Amps Does an Electric Dryer Require?
Most residential electric dryers require a 30-amp circuit, but higher-powered dryers can need 40 or 50 amps. The required amperage depends on the dryer’s power consumption and features such as steam cycles or high heat settings. Using a circuit with insufficient amperage can cause breaker trips or damage to the appliance. On the other hand, oversized circuits without proper wire sizing may pose safety risks. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications and NEC guidelines before installation.
Typical Voltage Requirements for Electric Dryers
Modern electric dryers are typically designed to operate on 220V to 240V. Older or smaller models may function on 110V to 120V circuits, though these are less common and often limited to gas dryers. The voltage requirement affects wire selection and breaker size, as higher voltage circuits demand thicker wires to safely carry the load. Ensuring the correct voltage is connected to your dryer is crucial for proper operation and longevity.
Difference Between 110V/120V and 220V/240V Dryer Circuits
110V/120V circuits are generally used for low-power appliances or gas dryers. These circuits draw less current and use smaller wires. In contrast, 220V/240V circuits are standard for electric dryers, delivering higher power to heating elements and motors. The higher voltage allows the dryer to operate efficiently while using fewer amps, reducing the risk of overheating wires. Choosing the proper voltage circuit prevents inefficiency, energy waste, and potential hazards.
What Size Wire Is Used for a 30-Amp Dryer?
For a 30-amp dryer, 10 AWG copper wire is typically recommended. If using aluminum wire, an 8 AWG conductor is required due to aluminum’s lower conductivity. Proper wire sizing ensures that the dryer receives adequate current without overheating the wires or tripping the breaker. Always pair the correct wire size with the appropriate breaker rating to comply with NEC safety standards.
Recommended Wire for a 40-Amp Dryer
A 40-amp dryer requires 8 AWG copper wire or 6 AWG aluminum wire. This increased size accommodates the higher amperage drawn by more powerful dryers. Using the correct wire prevents insulation damage, overheating, and potential fire hazards. When installing a 40-amp circuit, it is essential to use both the correct wire gauge and an appropriately rated breaker to maintain safety and performance.
Choosing Wire Size for a 50-Amp Dryer
For 50-amp dryers, 6 AWG copper wire or 4 AWG aluminum wire is recommended. These larger wires safely carry the high current needed for commercial or industrial-grade dryers. Improper sizing can lead to excessive heat, tripped breakers, or even electrical fires. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and NEC guidelines before selecting wire size for high-amp appliances.
Copper vs. Aluminum Wire for Dryers
Copper wire is a superior conductor, providing lower resistance and better durability. Aluminum wire is lighter and less expensive but requires careful installation due to its tendency to oxidize and expand. Both materials are suitable for dryer circuits if installed correctly, but copper is generally preferred for smaller residential circuits, while aluminum may be used in longer runs or larger circuits. Proper installation techniques are essential to avoid hazards.
Advantages of Using Copper Wire for Dryers
Copper wire is highly conductive, which means it carries electricity more efficiently than aluminum. It is also more durable, resistant to corrosion, and less likely to expand or contract under high heat. These properties make copper ideal for residential dryer circuits where safety and reliability are critical. Additionally, copper wire connections are easier to secure in outlets and breakers, reducing the risk of loose connections that can lead to sparks or fire. While copper is more expensive than aluminum, its longevity and superior performance often justify the investment.
Advantages of Using Aluminum Wire for Dryer Circuits
Aluminum wire is lighter and generally less expensive than copper, making it a practical option for larger or longer dryer circuits. Aluminum’s lower weight can simplify handling and installation, especially in commercial or industrial settings. However, aluminum requires special connectors and careful tightening to prevent oxidation and potential overheating. When installed correctly, aluminum wire can safely carry the high amperage required for dryers, offering a cost-effective alternative to copper in specific scenarios.
How Ampacity Affects Wire Selection
Ampacity refers to the maximum amount of electrical current a wire can safely carry without overheating. Choosing a wire with insufficient ampacity for your dryer can cause insulation to melt, trip breakers, or even create fire hazards. Conversely, selecting a wire with excessive ampacity is safer but can be unnecessarily expensive and harder to handle. Understanding ampacity is essential when selecting wire size for your dryer to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safe operation.
Understanding NEC Guidelines for Dryer Wiring
The National Electric Code (NEC) sets standards for safe wiring practices, including dryer circuits. NEC guidelines specify wire sizes, breaker ratings, outlet types, and grounding requirements. For example, a 30-amp dryer must use 10 AWG copper or 8 AWG aluminum wire, connected to the appropriate breaker. Following NEC guidelines is not only a legal requirement but also a critical safety measure. Improper wiring can lead to electrical hazards, insurance issues, and code violations.
3-Prong vs 4-Prong Dryer Outlets
Older dryers often use a 3-prong outlet, which combines neutral and ground connections in one wire. Modern dryers use a 4-prong outlet that separates neutral and ground for enhanced safety. The 4-prong design reduces the risk of electric shock and is now required for all new dryer installations. Understanding the difference between these outlets is crucial when replacing a dryer or upgrading wiring to meet current standards.
History of 3-Prong Dryer Outlets
Before 1996, most homes were wired with 3-prong dryer outlets, consisting of two hot wires and a combined neutral/ground wire. These outlets were safe at the time but did not separate grounding and neutral paths, which increased the risk of shock under certain conditions. While 3-prong outlets still function, modern safety standards favor 4-prong configurations. Homeowners with older outlets may need to upgrade to meet current electrical codes.
Benefits of Upgrading to a 4-Prong Dryer Outlet
Upgrading to a 4-prong outlet improves safety by providing a separate ground wire, reducing the chance of electrical shock. It also ensures compliance with NEC standards, which is especially important for insurance and resale value. A 4-prong outlet provides better protection for both the appliance and the user, preventing damage to the dryer or surrounding electrical system. Upgrading may require rewiring, but the safety benefits far outweigh the costs.
How to Determine If Your Dryer Outlet Needs Rewiring
To determine if your dryer outlet requires rewiring, check the number of prongs and the age of the installation. If the outlet is a 3-prong type and your dryer requires a 4-prong connection, rewiring may be necessary. Also, inspect the wire condition for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating. Consulting local electrical codes and a licensed electrician ensures that any upgrades meet safety standards and function correctly.
How to Safely Upgrade Your Dryer Circuit
Upgrading a dryer circuit involves installing the correct wire size, breaker, and outlet type. Always turn off power at the main panel before starting work. Use copper or aluminum wire with proper ampacity, and ensure all connections are tight and secure. Installing a 4-prong outlet for modern dryers enhances safety, and following NEC guidelines prevents code violations. For complex upgrades, hiring a licensed electrician is recommended to ensure compliance and safety.
Choosing NM-B Wire for Dryer Installation
NM-B wire, commonly called Romex, is widely used for dryer installations in residential settings. It is easy to work with, suitable for dry interior locations, and comes in pre-assembled cables with multiple conductors. NM-B wire is available in sizes like 10/3, 8/3, and 6/3, which correspond to the ampacity requirements of 30, 40, and 50-amp dryer circuits. Selecting the correct NM-B wire ensures compliance with NEC standards and provides a safe, reliable connection to your dryer.
Recommended NM-B Wire Sizes for Electric Dryers
For 30-amp circuits, 10/3 NM-B cable is recommended. For 40-amp circuits, 8/3 NM-B cable should be used, and for 50-amp circuits, 6/3 NM-B cable is ideal. Each cable includes the necessary hot, neutral, and ground conductors required for a 4-prong dryer connection. Using the correct cable size ensures that your dryer receives proper amperage and reduces the risk of overheating or tripping breakers, maintaining both performance and safety.
Using 10/3 NM-B Cable for 30-Amp Dryers
The 10/3 NM-B cable is designed specifically for 30-amp circuits. It includes two hot wires, a neutral, and a ground conductor, which makes it compatible with modern 4-prong dryer outlets. This cable size is ideal for standard household dryers and ensures that the circuit can handle the dryer’s electrical load without issues. Proper installation involves securely fastening the wires in the breaker panel and outlet, following NEC guidelines.
Using 8/3 NM-B Cable for 40-Amp Dryers

For dryers that require a 40-amp circuit, 8/3 NM-B cable is recommended. The thicker wire safely handles the increased current drawn by higher-powered dryers. Installation requires connecting each conductor correctly to the corresponding breaker and outlet terminals. Using 8/3 cable ensures the circuit operates efficiently, minimizes voltage drops, and prevents overheating, enhancing both safety and dryer performance.
Using 6/3 NM-B Cable for 50-Amp Dryers
High-powered dryers or commercial-grade appliances often need a 50-amp circuit. In such cases, 6/3 NM-B cable is the best choice. This cable can handle the heavy current without excessive heating, ensuring safe operation over long periods. Properly securing the connections and following NEC wiring standards are critical when installing 50-amp dryer circuits, as even minor mistakes can cause serious electrical hazards.
Why 10/4, 8/4, or 6/4 Cables Are Not Recommended
Cables with four conductors like 10/4, 8/4, or 6/4 are typically not used for standard dryer installations. The extra conductor is unnecessary for a 4-prong dryer outlet and may lead to confusion during installation. Using the correct 3-conductor cable with a separate ground ensures proper connections, simplifies wiring, and meets NEC requirements. Avoiding the wrong cable reduces mistakes and enhances overall safety.
Using THHN/THWN Wires in Conduit for Dryers
THHN and THWN wires are individual conductors used within conduit systems, offering extra protection for dryer circuits. These wires are ideal for surface-mounted or exposed installations where NM-B cables are not suitable. Conduit provides mechanical protection, reduces risk of damage, and ensures code compliance. When using THHN/THWN wires, make sure to select the appropriate gauge to match the dryer’s amperage requirements.
Surface-Mount Dryer Installations with Individual Wires
In some installations, dryers may be mounted on surfaces like concrete or brick walls. In these cases, using individual THHN/THWN wires inside conduit is preferred. This method protects the wires from physical damage, moisture, and abrasion. Proper conduit installation ensures both safety and durability while maintaining compliance with electrical codes. It also allows easier maintenance or upgrades in the future.
How Conduit Protects Dryer Wires
Conduit shields wires from external damage such as impact, moisture, and UV exposure. It also provides an organized pathway for wires, reducing the risk of accidental disconnections. For dryer circuits, conduit is particularly useful in garages, basements, or commercial areas where wires may be exposed. Using conduit ensures the long-term safety and reliability of your dryer installation while complying with NEC standards.
Can You Use Aluminum Wire for a 30-Amp Dryer?
While aluminum wire can technically be used for 30-amp dryer circuits, it is less ideal than copper due to lower conductivity. Aluminum requires careful handling, proper connectors, and frequent inspection to prevent oxidation or loose connections. For shorter runs, copper is preferred, but aluminum can be used if cost or availability makes it necessary. Ensuring proper installation practices is crucial for safety.
Aluminum Wire for 40-Amp and 50-Amp Dryer Circuits
Aluminum wire is commonly used for 40-amp and 50-amp dryer circuits because it is lighter and more cost-effective than copper. For these higher-amperage circuits, aluminum’s slightly lower conductivity is offset by using a larger gauge wire (6 AWG for 40-amp, 4 AWG for 50-amp). Proper installation is crucial, including using anti-oxidant compound on connections and tightening terminals to manufacturer specifications. With careful handling, aluminum provides a safe and reliable solution for high-amp dryer circuits.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum Dryer Wire
Aluminum wire is less expensive and lighter than copper, making it ideal for long runs or commercial installations. However, it expands and contracts more than copper, which can loosen connections over time if not installed properly. Copper wire, while more expensive, offers superior conductivity, durability, and lower maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on budget, wire run length, and local electrical codes, but safety should always be the top priority.
How Wire Length Affects Dryer Performance
Longer wire runs can result in voltage drops, which reduce dryer efficiency and increase energy consumption. To compensate for long runs, electricians may use a thicker gauge wire to maintain adequate voltage at the appliance. Incorrect wire length or undersized cables can lead to overheating, tripped breakers, or decreased dryer performance. Measuring and planning wire runs before installation is essential to ensure optimal operation.
Wire Termination: Secure Connections for Safety
Proper termination of dryer wires at the breaker panel and outlet is critical for safety. Loose connections can cause arcing, overheating, or electrical fires. Always strip wires to the correct length, insert them fully into terminals, and tighten screws to manufacturer specifications. Using a torque screwdriver when required ensures connections meet safety standards. Well-terminated wires protect both the appliance and your home from hazards.
Risks of Using Undersized Wire for Your Dryer
Using a wire smaller than the recommended gauge for your dryer creates a serious fire risk. Undersized wire can overheat, melt insulation, and damage the dryer or surrounding surfaces. It may also cause breakers to trip frequently, reducing appliance efficiency. Ensuring that the wire matches the dryer’s amperage rating is essential for safe and reliable operation.
What Happens If the Dryer Wire Is Too Large?
While oversized wire is safer in terms of current capacity, it can be harder to handle and more expensive. Large wires are less flexible, making connections more difficult in tight spaces. However, using a wire slightly larger than required is not dangerous and can offer added safety margin. The key is to balance ease of installation, cost, and electrical requirements.
Importance of a Dedicated Circuit for Electric Dryers
Electric dryers require a dedicated circuit to operate safely and efficiently. Sharing the circuit with other appliances can overload wires, trip breakers, and create fire hazards. A dedicated circuit ensures that the dryer receives consistent power and reduces the risk of electrical interference or damage. NEC guidelines emphasize dedicated circuits for all major appliances, including dryers.
How Breaker Size Matches Dryer Wire Size
The circuit breaker must match the wire size and dryer amperage to ensure safe operation. For instance, a 30-amp dryer using 10 AWG copper wire should be protected by a 30-amp breaker. Matching breaker size prevents overloading, overheating, and potential fire hazards. Incorrect breaker sizing can void warranties, cause electrical issues, and compromise safety.
Signs Your Dryer Circuit Is Overloaded
An overloaded dryer circuit may trip breakers frequently, cause the dryer to run slowly, or produce unusual smells. Flickering lights or buzzing sounds near the outlet are also warning signs. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent serious electrical hazards. Upgrading wire size or installing a dedicated circuit may be necessary to resolve overload issues safely.
Avoiding Extension Cords for Electric Dryers
Using extension cords with electric dryers is extremely unsafe. Dryers draw high current, and standard extension cords cannot handle the load. This can lead to overheating, melting insulation, and fire hazards. Always connect the dryer directly to a properly installed outlet with the correct wire size and breaker protection.
Why Portable Power Cords Are Unsafe for Dryers
Portable power cords are designed for temporary, low-current applications, not continuous high-amperage use. Connecting a dryer to such cords can overheat the wires, damage the appliance, and create fire risks. Using a dedicated, properly wired outlet is essential for safety and code compliance. Avoid shortcuts to ensure long-term protection.
Common Mistakes When Installing Dryer Wires
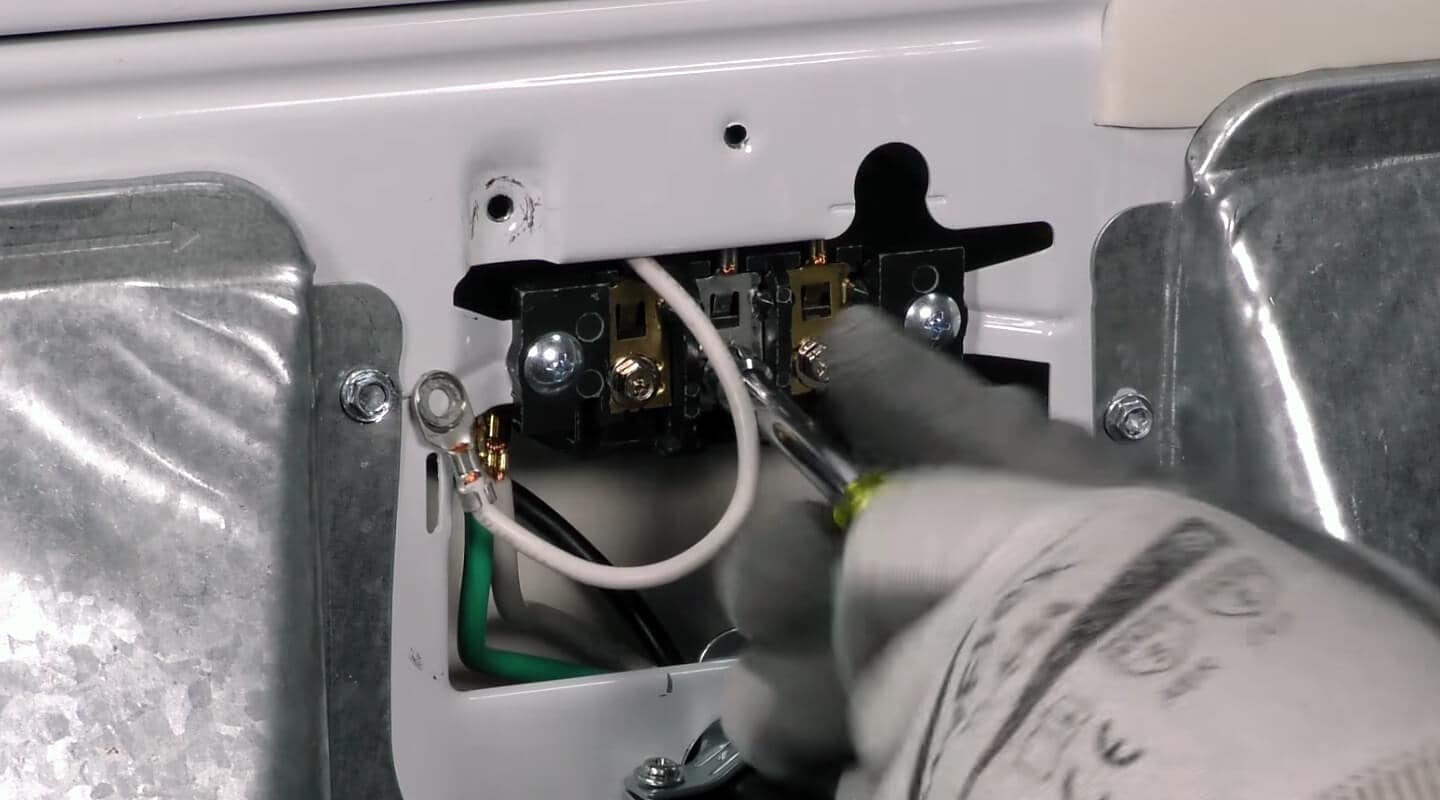
Mistakes like using the wrong wire gauge, improper grounding, loose connections, or incorrect outlet types can compromise dryer safety. Common errors also include using old 3-prong outlets with modern dryers or improperly connecting aluminum wires. Following NEC guidelines and manufacturer instructions helps prevent these issues and ensures a safe, reliable installation.
Tips for Proper Dryer Wire Installation
Always turn off power before installation, measure wire runs accurately, and choose the correct wire gauge. Use proper tools, follow color codes, and double-check all connections. Installing the correct breaker and outlet type completes a safe circuit. Proper planning and adherence to code requirements are key to a successful and safe dryer installation.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct wire size for your electric dryer is essential for safety, efficiency, and compliance with the National Electric Code. Whether using copper or aluminum wire, following proper ampacity guidelines and choosing the right breaker and outlet type ensures reliable performance. Upgrading older 3-prong outlets to 4-prong connections enhances safety, while using the proper NM-B or THHN/THWN cables protects your home from electrical hazards. By carefully planning your dryer wiring, securing all connections, and following manufacturer and NEC guidelines, you can enjoy safe, efficient, and long-lasting dryer operation in your home.
FAQs
1. What wire size is needed for a standard 30-amp electric dryer?
For a 30-amp dryer, 10 AWG copper wire or 8 AWG aluminum wire is recommended. This ensures safe current flow without overheating or tripping the breaker.
2. Can I use aluminum wire for my dryer?
Yes, aluminum wire can be used, especially for higher amperage circuits like 40-amp and 50-amp dryers. Copper is generally preferred for 30-amp circuits due to its conductivity and reliability.
3. What is the difference between 3-prong and 4-prong dryer outlets?
A 3-prong outlet combines neutral and ground wires, while a 4-prong outlet separates neutral and ground. Modern dryers require 4-prong outlets for improved safety.
4. Can I use a 10/4 NM-B cable for my dryer?
No, 10/4 cables are not recommended for standard dryer installations. Use 10/3, 8/3, or 6/3 NM-B cables based on the dryer’s amperage.
5. What breaker size should I use for a 40-amp dryer?
A 40-amp dryer requires a 40-amp breaker, paired with 8 AWG copper or 6 AWG aluminum wire to safely handle the load.
6. Can I run my dryer on a 110V/120V circuit?
Most electric dryers require 220V/240V circuits. 110V/120V circuits are typically reserved for gas dryers and lower-powered appliances.
7. Is it safe to use an extension cord with a dryer?
No, extension cords are unsafe for high-current appliances like dryers. They can overheat and cause fires. Always connect the dryer to a properly wired outlet.
8. How long can dryer wires be before voltage drop becomes an issue?
Longer wire runs may require a larger gauge to compensate for voltage drop. For most residential installations, keeping the run under 50 feet is recommended, but exact requirements depend on the dryer’s amperage.
9. What type of wire is best for a surface-mounted dryer outlet?
THHN/THWN wires inside conduit are recommended for surface-mounted installations, providing extra protection from physical damage and compliance with code.
10. Should I hire an electrician to install dryer wiring?
While experienced DIYers can install dryer wiring, hiring a licensed electrician ensures proper installation, NEC compliance, and maximum safety, especially for high-amperage circuits.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on premiumtechy!



